EPC project companies operate with profit margins to the tune of 6 to 7% where as around 12% of the payments fall into the category of retention. The ability to claim the retention payments and other claims faster is of prime importance to maintain healthy project cash flows, towards the closing stages of projects.
Can application of agile best practices help?
As the industry is abuzz with the topic ‘Agile Vs Classical project management’, we would like to embrace ‘Agile & Classical project management’. After in-depth practice and research of Agile (Adaptive) and Classical (Predictive) project management (PMBOK, TCM, PRINCE2 etc) over a decade, we can vouch for the effectiveness of the application of agile best practices within predictive (classical) project management. The most significant benefit is the improved predictability of milestones achievement, which include the billing milestones. This in turn improve cash flow of projects.
What is Agile Project Management (APM)?
The roots of Agile Project Management (APM) is in the Information Technology related projects. Though I.T started with the classical project management approaches, soon they realized that it does not hold good for projects were requirements are continuously evolving and technology is rapidly changing. That resulted in the evolution of multiple frameworks like SCRUM, XP, RUP, TDD, FDD etc under the umbrella Agile Project Management (APM). The common thread running across all these frameworks is the iterative approach to developing the product of the project. For all our further discussions on agile, I will use the ‘SCRUM’ framework, which is the most popular framework within the APM family and is domain independent. Many ceremonies within the SCRUM framework are easily applicable within the classical (predictive) project management practices followed by EPC Projects.
Building blocks of SCRUM
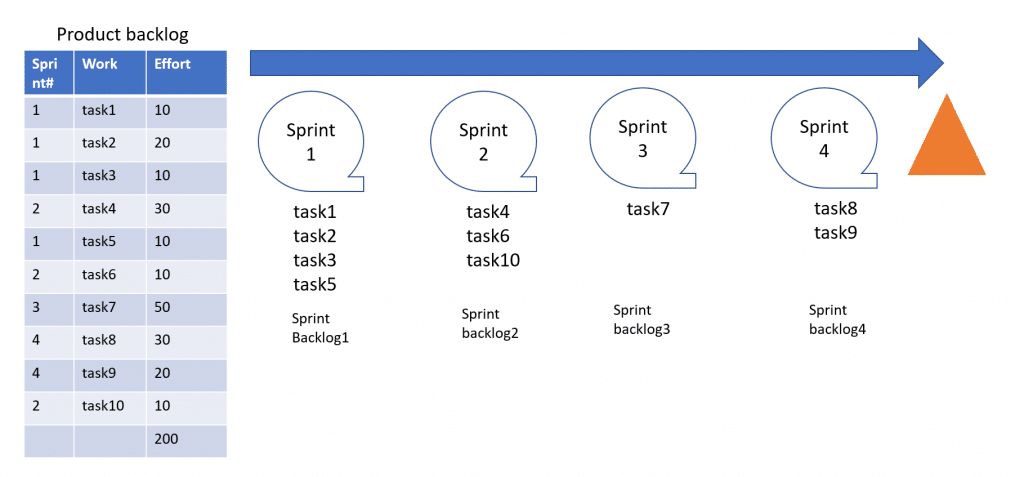
Product backlog ( Work to be completed till the milestone)
From an EPC, project perspective, Product backlog is the list of work to be completed till the completion of the scope of the project, or towards the achievement of a major milestone. The table below is a sample product backlog. To simplify things for the EPC projects, one can consider this as a master list of pending tasks to be completed till the achievement of the upcoming billing milestone.
| Sprint # | Work | Effort |
| 1 | task1 | 1 |
| 1 | task2 | 20 |
| 1 | task3 | 10 |
| 2 | task4 | 30 |
| 1 | task5 | 10 |
| 2 | task6 | 10 |
| 3 | task7 | 50 |
| 4 | task8 | 30 |
| 4 | task9 | 20 |
| 2 | task10 | 10 |
| 200 |
Sprint backlog (Work to be completed within the sprint)
As discussed before, agile projects advances incrementally through iterations. In SCRUM framework, these iterations are known as Sprints. Sprints are time buckets . The duration of sprints can be weekly, fortnightly or monthly. But never more than 30 days. This is because agile promotes fast failures, because faster you fail, there is more time to correct and the cost of rework is lesser than failing later.
Sprint backlogs are the subset of the product backlog which the team has committed to complete within the sprint. Before the start of every sprint, the scrum team (cross disciplinary) gets into a sprint planning meeting which is time boxed to 8 hours. The output of the sprint planning meeting is the sprint backlog which is prioritized, estimated and committed list of tasks the team has agreed to complete within the sprint.
Eisenhower Decision matrix
Eisenhower decision matrix provides us with a method to prioritize tasks based on importance and urgency.
Eisenhower matrix helps us to classify activities as;
- Important & Urgent
- Important & Not urgent
- Not Important & Urgent
- Not Important & Not urgent
As and when the project approaches major milestones, especially billing milestones, the remaining tasks to be completed must be prioritized based on impact on critical path, impact on milestone, float availability to form a urgent and important task list (equivalent to the product backlog) which can be further prioritized into sprints (iterations).
Though this approach is very effective while approaching any major milestone, this can be easily implemented to manage issues , snags which has maximum impact on releasing the retention amounts.
Monitoring & Controlling
Agile Project Management (APM) teams have fixed time, fixed duration daily meetings (scrum) where the team members discusses progress and the problems. This helps in faster issue resolution and transparency. Another tool which drives the team to the target is the burn down charts. On the ‘X’ axis of the burn down chart is the duration of the sprint (distance to the finish line) and on the ‘Y’ axis, the values can be number of tasks to be completed, weight-age of the tasks to be completed or the balance effort required to complete the sprint backlog.
At the end of every sprint, the output of the sprint is formally reviewed. The lessons learned during the sprint are captured which are used during the subsequent sprint planning meeting.
Application of Earned Value Management and Earned Schedule Management system along with Burn down charts will help to proactively address schedule and cost variances.
Lessons learned from an EPC project (power grid) where agile best practices were implemented;
Project details
- 7 – 12 engineers working together
- Cost and Schedule is almost fixed
- Principal engineering (drawings)
- Approval by Customer
- Detailed engineering
- Throughout the design phase, engineering and purchase work together
- Teams were distributed in Vaasa, India , Estonia
Benefits reported
- Increased communication within and across teams
- The visibility and ability to follow what the team is doing is at a whole other level
- The transparency to others outside the team is close to perfect
- People only work on tasks that are on the task list, and these are in a prioritized order
- When stakeholders see what tasks are on the task list and what priority their task has in relation to other tasks, they become more patient with waiting for their task to be finished
- Builds better relations between the team and their internal customers
- With the opportunity to bring forth problems in daily meetings, the transparency has increased a lot
- Problems surface quite quickly, allowing them to be solved faster
- The problems are often identified by the team
- When a problem is brought to the team’s knowledge during the daily meetings, others can immediately help with the problem
- If a change is in conflict with another change it can be spotted as soon as possible
- If a problem then surfaces it is easy to find , since only one day’s work has to be gone through to find the problem and people still remember well what they have done during the day
- A project can last for 1.5 years and previously feedback wasn’t gathered into a final report until the end of the project. This feedback could then be utilized to improve future projects. Today thanks to Scrum this cycle is much faster and they ask for and discuss feedback continuously
- Process improvement activities have become part of the project
- Unified the ways of working
- Business development efforts are also accounted
Conclusion
By applying the Agile Project Management (APM) best practices within the classical project management (traditional project management) helps to focus on the urgent and important tasks. Tasks can be prioritized as urgent and important , based on whether they are on the critical path, float availability, degree of impact on billing milestones etc. This systematic prioritization of tasks and finishing them off with top priority is possible by applying agile project management best practices within the predictive / classical project management. This approach enhances milestone accomplishment and the cash flows of the project.